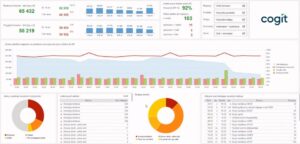
Cogit Planning and Scheduling Modules
The system is divided into two main modules responsible for sales forecast preparation and optimal planning of deliveries to sales points.
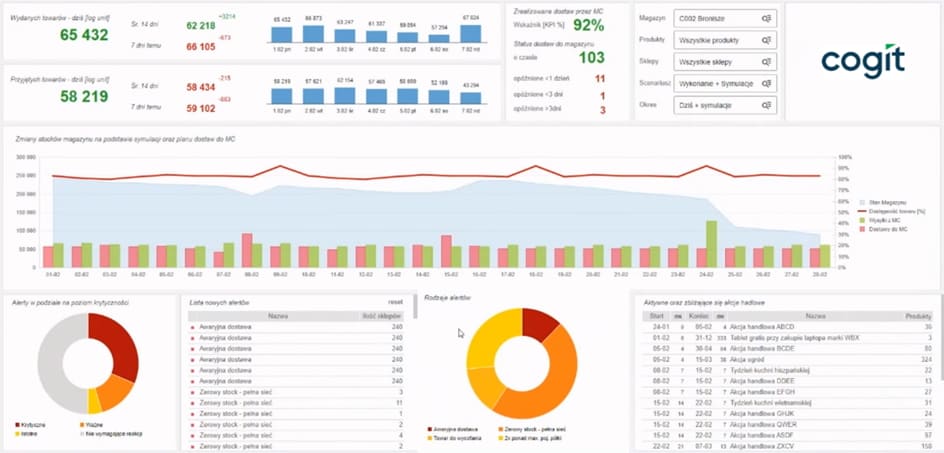
Based on data from inventory levels, daily sales, historical data, forecasts, and a series of parameters, the system decides on the delivery of a particular product. For this purpose, the system calculates hundreds of millions of combinations of data daily (or at a specified interval) and generates forecasts for the state of each item on each shelf for subsequent periods. The result is a delivery plan ensuring product availability or the fulfillment of other expected quality parameters.
Key functions of the process are executed by the system, and users, instead of tedious planning, can focus on parameterization and handling exceptional situations that require changes to plans generated by the system.
Delivery Planning and Forecasting Module
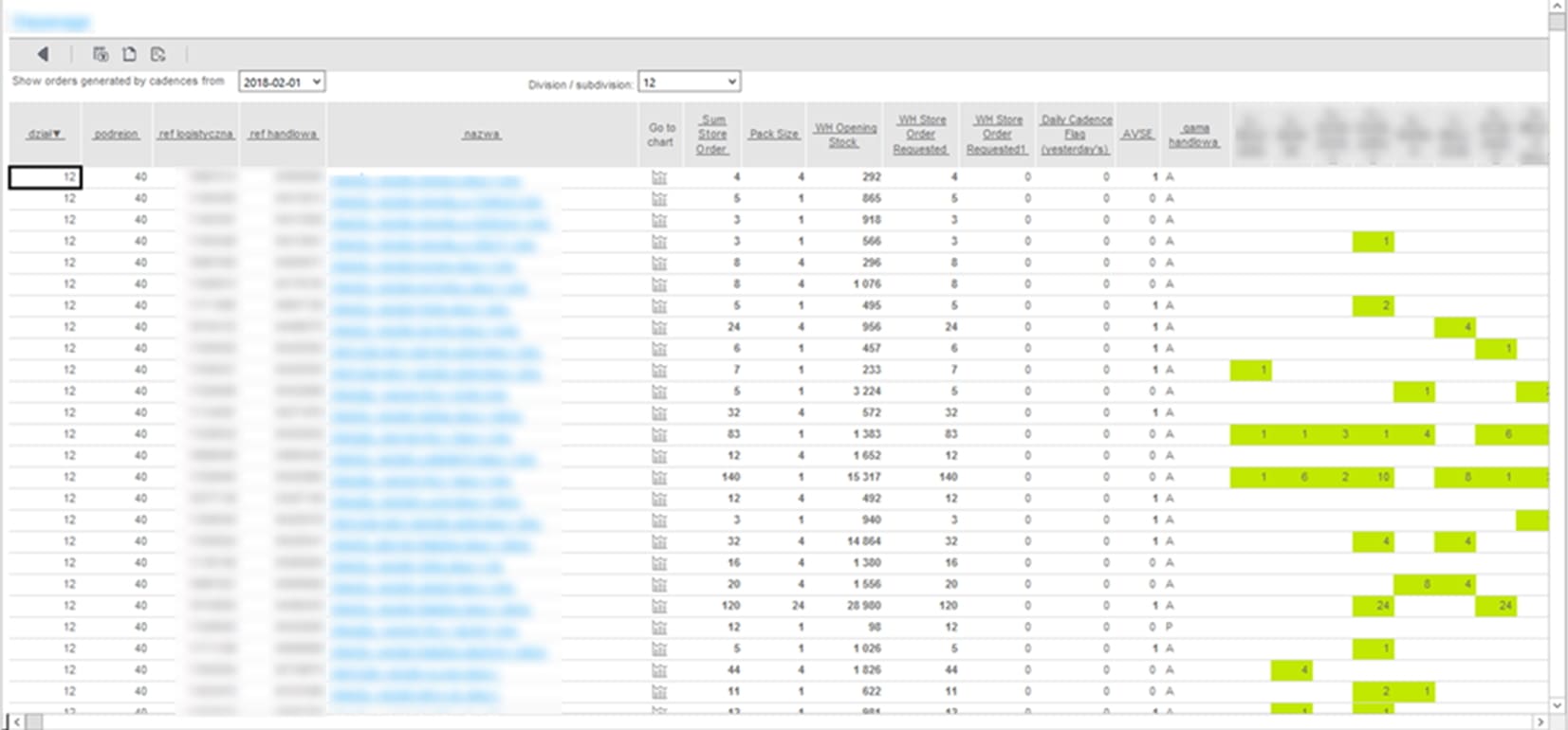
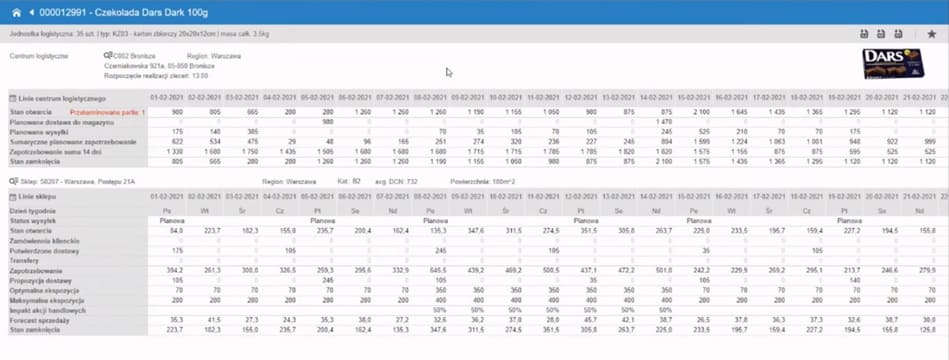
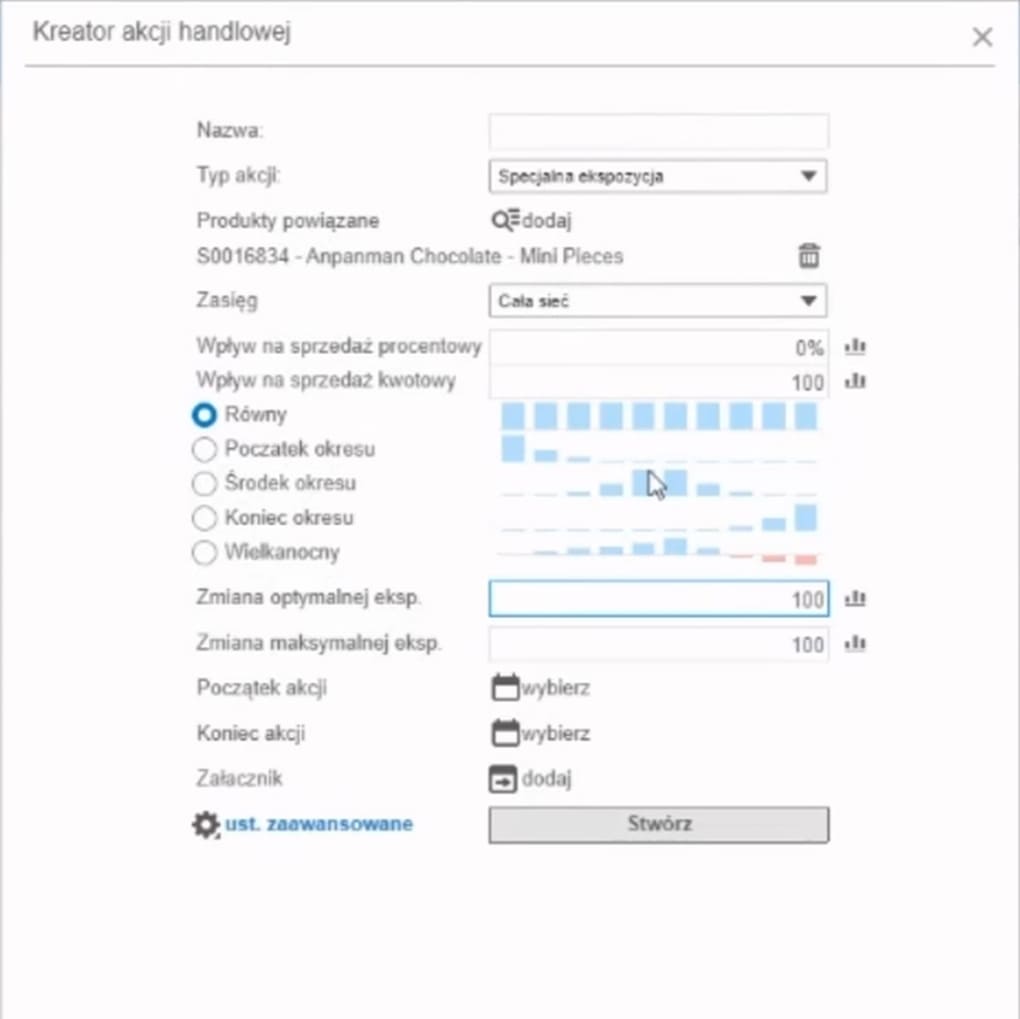
The main goal of the module is to generate optimal orders for selected references. Factors taken into account include planned demand, delivery time, shelf and exposure capacities. Additionally, in the case of shortages in the central warehouse, the system ensures equitable rationing of goods among stores.
With appropriate parameterization, the system operates fully automatically without requiring manual user intervention.
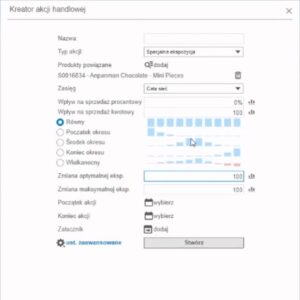
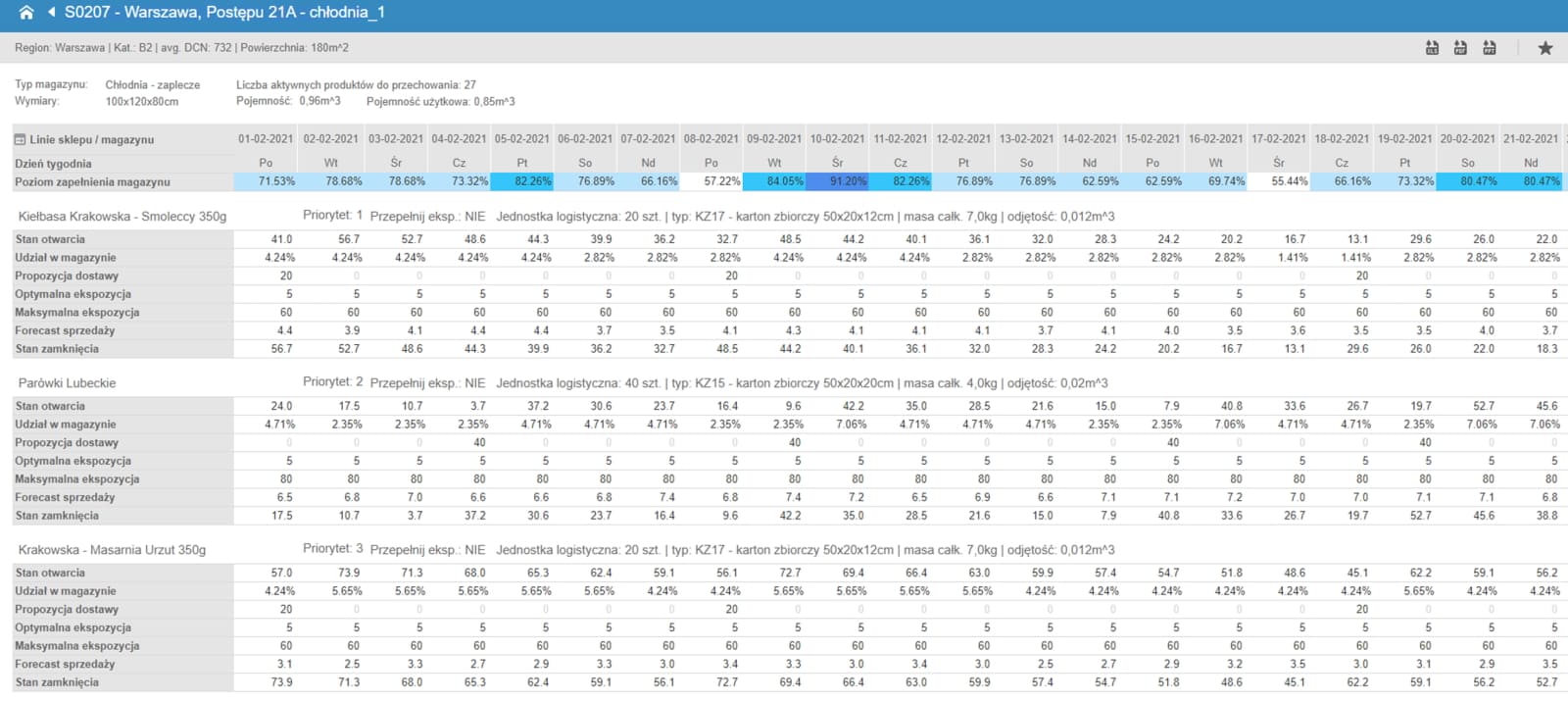
A key factor driving orders is the set of exposure parameters. Their selection allows the system to optimally match orders to maintain the level of goods at the point of sale within the expected range of optimal exposure.
Additionally, exposure enables the control of order sizes (replenishment) for planning:
- Promotions and sales campaigns
- Reconstructions, additional “stands,” exposure changes.
- Additional demand reported by store managers.
Order Planning Cycle
Typically, the full cycle of calculations and order generation is carried out once a day. Results can also be generated on demand or in case of new source data or parameters.
Delivery Schedules
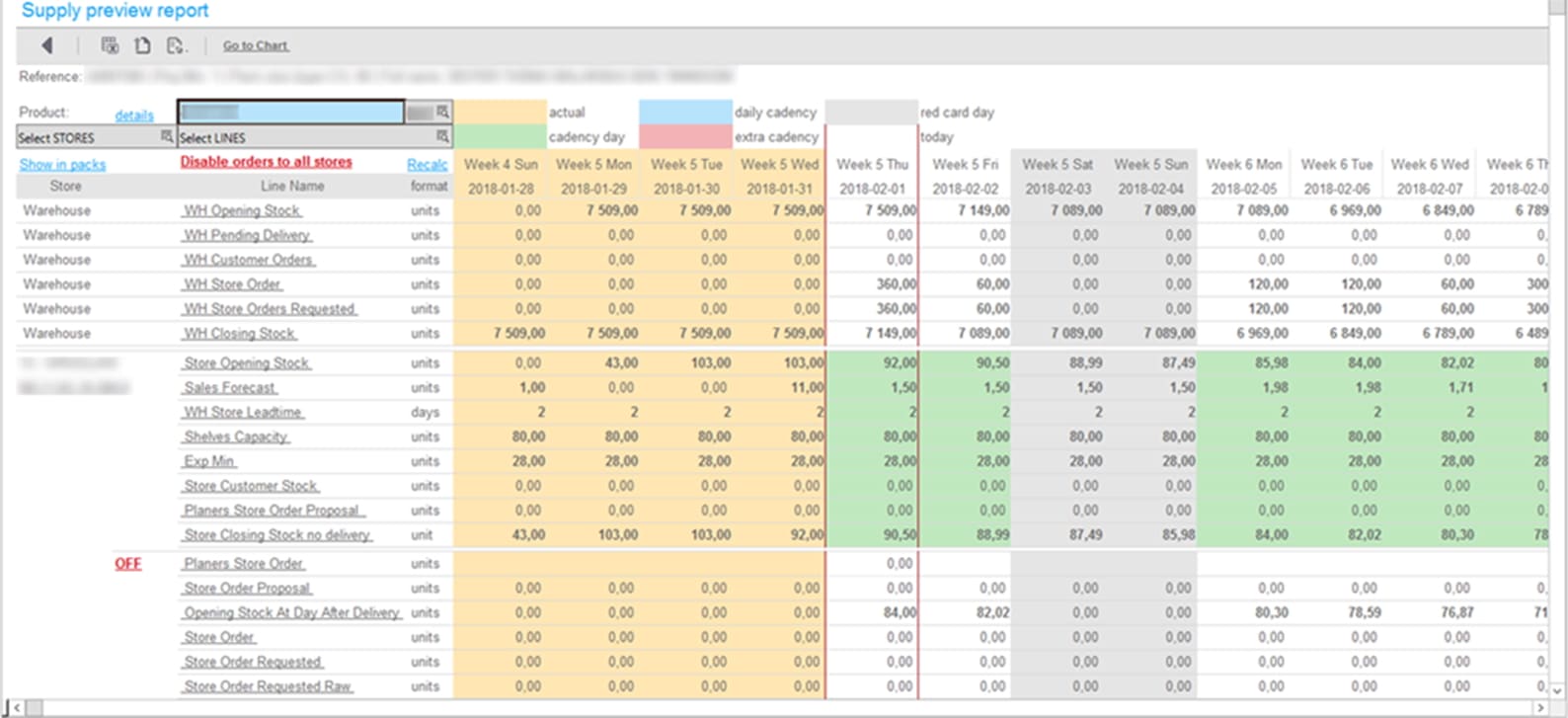
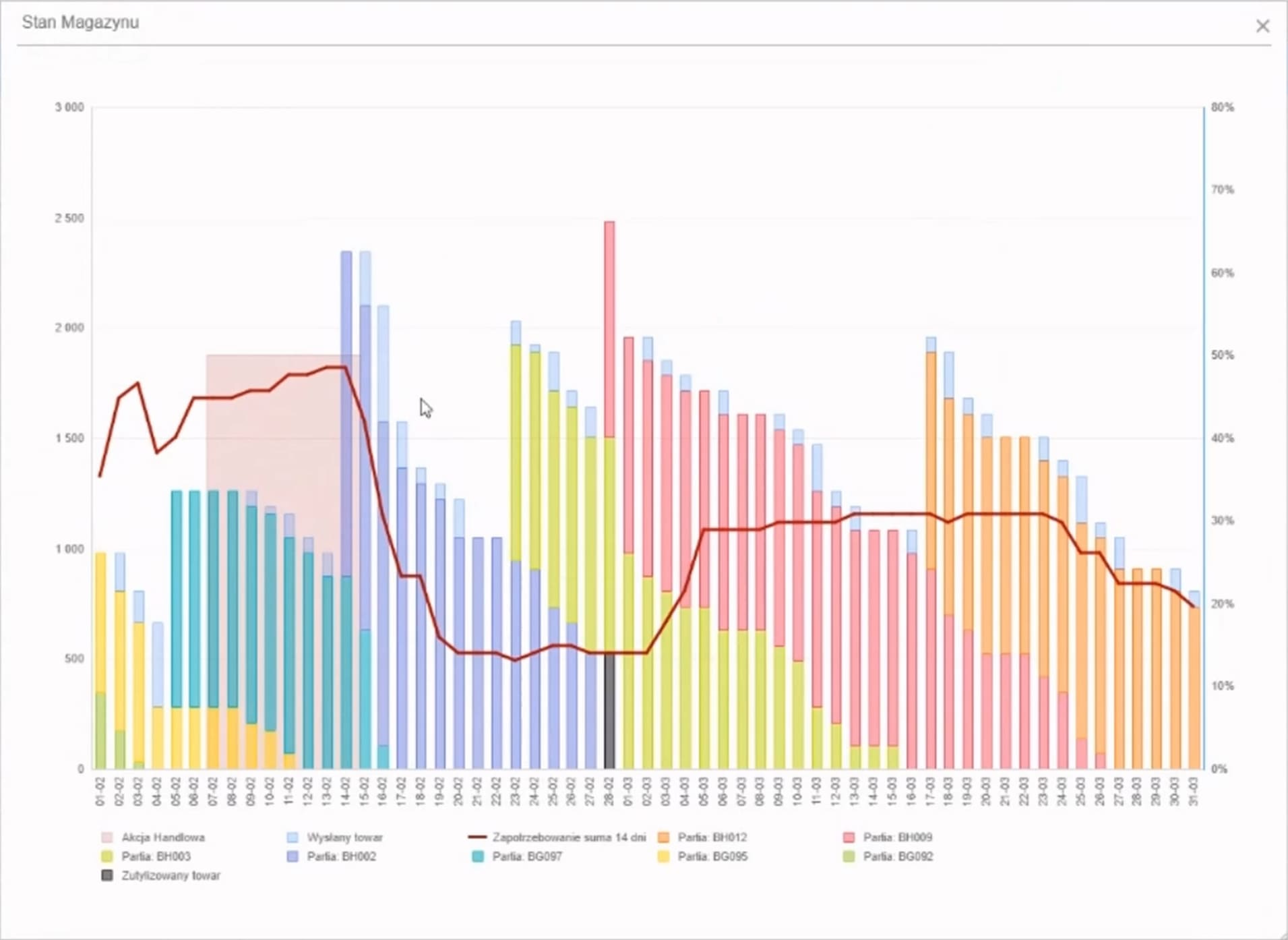
The delivery schedule to each sales point is dynamically calculated, impacting the size of orders generated by the system. When calculating the day on which goods can appear on the shelf, factors such as delivery cadence, calendar, and additional parameters are taken into account. The delivery schedule allows determining the period to cover sales.
Order Size
The basis for calculating the order size is the sum of the current stock in the store and the sales forecast for the required coverage period. Each product has a set of detailed parameters (e.g., logistics units) to determine other necessary factors affecting the order size.
Orders are optimized considering various parameters. The system ensures the best distribution of goods in the network in terms of sales volume and minimizes the possibility of interruptions in the availability of goods.
Additionally, the Delivery Planning and Forecasting Module provides many useful functionalities, such as:
- alerts about undesirable situations and assistance in mitigating their effects,
- management of products in stock,
- central warehouse,
- emergency plans and critical paths;
- establishing relationships between products,
- and many more.
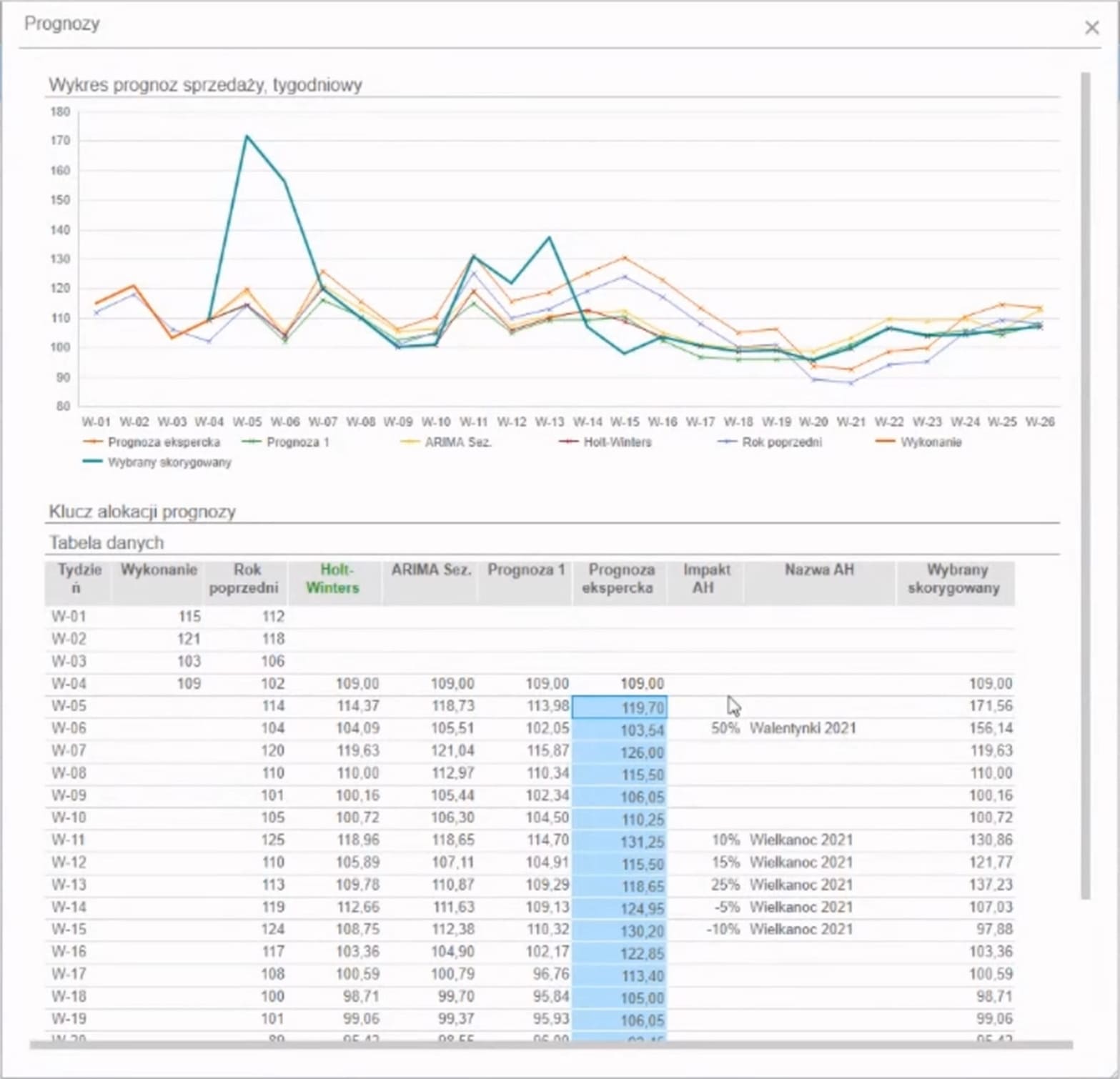
Sales Volume Forecasting Module
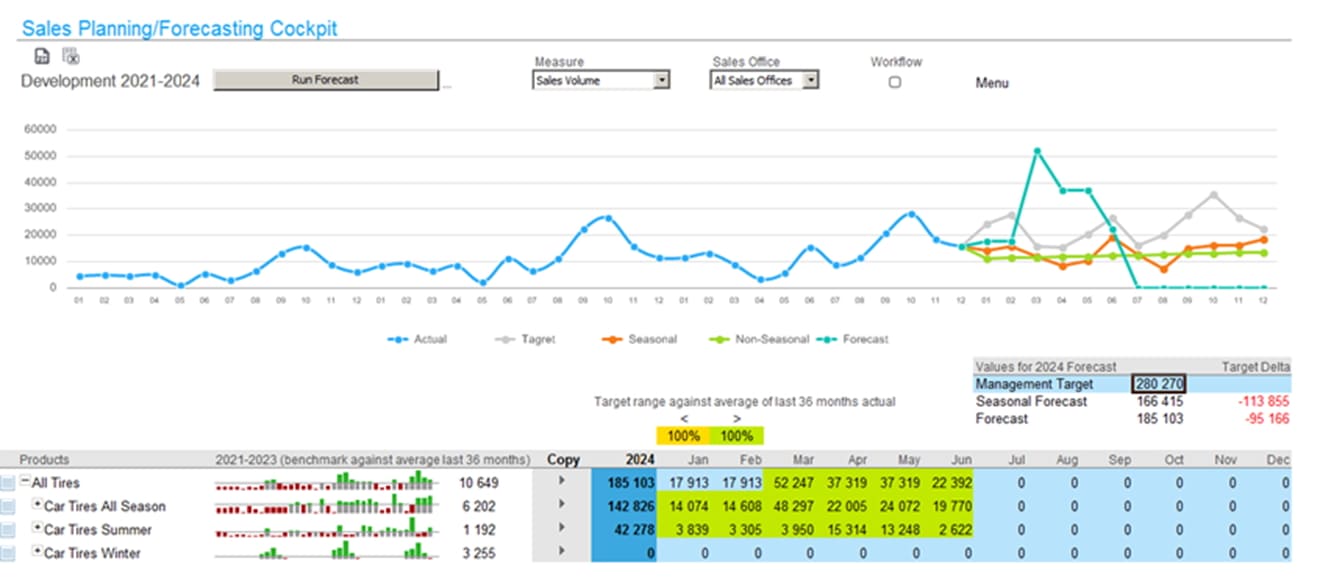
For sales forecasting, a multidimensional computational engine Infor OLAP is utilized. The database resides in memory, allowing for very high computational performance.
For more advanced statistical calculations, the integrated R language is used. This allows creating forecasts directly within the module’s model based on any data. Users can quickly and easily designate any subset of the multidimensional model as the basis for forecasting and the period for which the forecast is to be generated. R analyzes data according to the selected forecasting method.
Similar to integration with the R statistical computation engine, the forecasting module can also leverage external artificial intelligence-based computation systems.
Computational efficiency allows for the calculation of a separate forecast for each product and sales point, followed by the consolidation of all data. In the presence of sufficient historical data, forecast parameters can be enriched with any number of additional parameters and correlations. This approach allows for the optimal utilization of specific features at a detailed level (e.g., the sale of a specific product at a particular gas station) while simultaneously utilizing statistical methods on aggregated large volumes of data.
Available Forecasting Methods
The module typically allows forecasting based on the following methods:
- Previous period (year)
- Previous period +/- growth (decline) parameters
- Holt-Winters
- ARIMA
Generated forecasts can be parameterized regarding the utilization of seasonality and consideration of new product effects and atypical data disturbances.